
When it comes to saving for retirement, individuals have a range of options to choose from. Among the popular choices are self-directed individual retirement accounts (IRAs) and employer-sponsored 401(k) plans. Each of these retirement plans can benefit your retirement savings strategy. When you understand the differences between these plans, you can make more informed decisions about your future finances.
This article compares self-directed IRAs vs. solo 401(k) plans and covers their advantages and disadvantages.
Self-Directed IRA vs. Self-Directed 401(k)
In this section, we discuss self-directed IRAs vs. 401(k) plans.
Self-Directed IRA Overview
This is a retirement account type for individuals who want greater flexibility and control over their investing strategy. While traditional retirement plans tend to offer fewer investment vehicles like stocks and mutual funds, self-directed IRAs allow you to invest in a wider variety of investments. The following are key factors of a self-directed IRA:
- Tax advantages: Similar to conventional IRAs, a self-directed IRA can offer potential tax benefits. You can make tax-deductible contributions to traditional self-directed IRAs, so you may be able to lower your tax liability the year you make your contributions. The investment earnings within the account grow tax-deferred until you make withdrawals in retirement, at which point they are subject to ordinary income tax. Contributions to a Roth self-directed IRA are with after-tax dollars, then your qualified withdrawals in retirement are tax-free.
- Custodian requirement: Opening and operating a self-directed IRA requires a custodian to handle your administrative tasks and ensure your retirement account remains compliant with IRS regulations. Your custodian is responsible for maintaining records and processing transactions.
- IRS rules: The IRS limits how much you can contribute to a self-directed IRA, just as with conventional IRAs. You can contribute a maximum of $6,500 to your self-directed IRA each year. If you are 50 or older, you can contribute up to $7,500. With a self-directed IRA, you must adhere to the same regulations that come with a conventional IRA, such as required minimum distributions (RMDs). For a traditional IRA, you can only make contributions until you reach age 70 ½, while a Roth IRA has no age limit.
- Investment options: A self-directed IRA enables you to invest in a wide range of investment vehicles that go beyond conventional asset options like stocks and bonds. Alternative asset options you may be able to invest in with a self-directed IRA include precious metals, real estate, tax liens, private equity and cryptocurrencies.
Self-Directed 401(k) Overview
This retirement savings plan enables you to invest in a greater variety of asset options than you can with a traditional 401(k). A self-directed 401(k) is intended for self-employed individuals and small businesses that only employ the business partners. If you are self-employed, you can open a self-directed 401(k) retirement account and start making contributions.
With a self-directed 401(k), you can contribute to your plan as both employer and employee. The IRS limits how much you can contribute to your account. You are limited to an annual contribution amount of $22,500, or $30,000 if you are age 50 or older.
Investing in a self-directed 401(k) gives you greater control over the assets where your funds are invested. You can invest in traditional asset types like bonds and stocks, and you can also invest in alternative assets, such as real estate and precious metals.
Though this retirement plan can give you greater control over your investments, you may also face some risks. You could lose money if your investments decrease in value, and you may need to pay fees to open and maintain an account.
Pros and Cons of 401(k) vs. IRA
Learn the pros and cons of solo 401(k) vs. self-directed IRA plans:
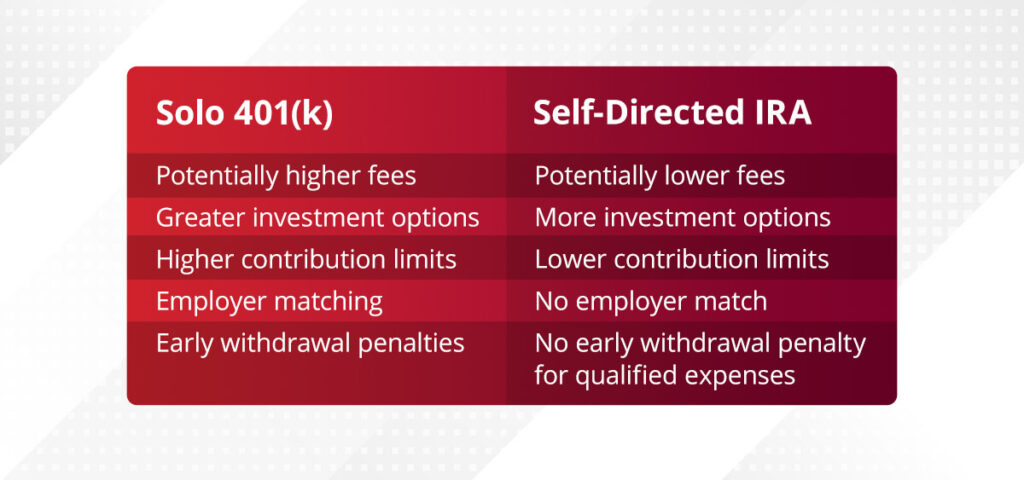
Pros and Cons of 401(k)
The advantages of 401(k) plans include the following:
- Higher contribution limits: The contribution limit for 401(k)s is higher than the contribution limit for IRAs.
- Employer matching: To incentivize employee retention and satisfaction, many employers offer a matching contribution to employees’ 401(k) plans. These matching funds can also increase your retirement savings. However, keep in mind that you can only have a self-directed 401(k) if you are self-employed.
- Automated contributions: When you have a 401(k), you can easily automate your contributions and save for your retirement.
- Greater investment options: Though self-directed 401(k) plans and IRAs typically offer a wider range of investment vehicles than traditional plans, a standard 401(k) plan tends to provide more investment options than a standard IRA.
The following are some of the disadvantages of a 401(k) plan:
- Potentially higher fees: A 401(k) plan may charge higher fees than other types of retirement plans.
- Early withdrawal penalties: If you make an early withdrawal before you reach age 59 ½, you may be required to pay a 10% early withdrawal penalty.
Pros and Cons of Self-Directed IRA
The following are the advantages of a self-directed IRA:
- Greater flexibility: IRAs tend to offer more flexibility than 401(k) plans regarding when you can contribute funds and withdraw your money.
- Potentially lower fees: IRAs also typically have lower fees than 401(k) plans.
- More investment options: Additionally, IRAs generally offer a wider range of investment options compared to 401(k) plans.
- No early withdrawal penalty for qualified expenses: As long as you use the funds for a qualified expense, you can withdraw money from your IRA without paying a penalty. Qualified expenses may include education costs, a first-time home purchase and medical expenses.
The disadvantages of a self-directed IRA include the following:
- Lower contribution limits: Typically, standard IRAs have a lower contribution limit than a 401(k), which means you may not be able to save as much for retirement each year.
- No employer match: Unlike 401(k)s, IRAs don’t offer an option for employer matching, so saving for retirement may be slower or more challenging.
Self-Directed Retirement Plans vs. Traditional Plans
The following are the benefits of self-directed IRAs and 401(k) plans over traditional retirement plans:
- Control: When you choose a self-directed retirement plan, you tend to have more control over how you invest your money. You can select the exact investments you prefer and take on more risks if you choose.
- Investment options: Compared to standard IRAs and 401(k)s, self-directed plans typically offer a wider range of investment vehicles.
- Risk: By investing in a self-directed IRA or 401(k), you can diversify your portfolio, which may reduce your overall risk for your retirement savings.
Fortunately, you don’t have to choose between a self-directed 401(k) and IRA — you can contribute to both. Keep in mind, though, that the contributions you make to a self-directed IRA may not be entirely tax-deductible depending on the contributions made to your 401(k), along with your adjusted gross income (AGI).

Schedule a Free Consultation With Accuplan
Choosing between a self-directed IRA and a 401(k) depends on your individual circumstances, preferences and investment goals. Schedule a free consultation from us at Accuplan to learn more about opening a retirement account.